Kaggle比赛 - Kannada MNIST
0 题目背景
比赛地址:Kannada MNIST
这是一个MNIST扩展的比赛,识别的不再是阿拉伯数字,而是Kannada数字,分类目标还是0-9,每个分类各有6000的样本,测试样本为5000的随机样本
1 数据分析
1.1 加载数据
%%time
train_data = pd.read_csv('/kaggle/input/Kannada-MNIST/train.csv')
test_data = pd.read_csv('/kaggle/input/Kannada-MNIST/test.csv')
1.2 查看label分布情况
label_values = train_data['label'].value_counts().sort_index()
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 3))
plt.title("Kanada MNIST label distributions")
sns.barplot(x=label_values.index, y=label_values)
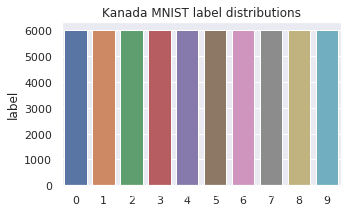 可以看出label分布一致
可以看出label分布一致
1.3 将csv数据转换成图像
img_train = train_data.drop(["label"], axis=1).values.reshape(-1, 28, 28, 1).astype('float32')
img_label = train_data["label"]
img_test = test_data.drop(["id"], axis=1).values.reshape(-1, 28, 28, 1).astype('float32')
print("img_train.shape = ", img_train.shape)
print("img_label.shape = ", img_label.shape)
print("img_test.shape = ", img_test.shape)
训练集包含60000张图片,测试集包含5000张图片
1.4 查看一下样本图片及其对应的label
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
show_img = 0
for idx in range(img_train.shape[0]):
plt.subplot(5, 5, show_img + 1)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.grid(False)
plt.imshow(img_train[idx].reshape(28, 28), cmap=plt.cm.binary)
plt.title("label: %d" % img_label[idx])
show_img += 1
if show_img % 25 == 0:
break

2 构建模型
2.1 搭建卷积神经网络
由于图片很小,不适合深层的卷积神经网络,所以只需要简单的几层卷积层和池化层就可以了,这里搭建一个6层卷积层,3层池化层,2层全连接层的卷积神经网络
def build_model(input_shape=(28, 28, 1), num_classes = 10):
input_layer = Input(shape=input_shape)
# 第一个卷积层,32个卷积核,大小5x5,卷积模式SAME,激活函数prelu
x = Conv2D(filters=32, kernel_size=(5, 5), padding="same", name="conv1")(input_layer)
x = PReLU()(x)
# 第二个卷积层,32个卷积核,大小5x5,卷积模式SAME,激活函数prelu
x = Conv2D(filters=32, kernel_size=(5, 5), padding="same", name="conv2")(x)
x = PReLU()(x)
# 第一层池化层,池化核大小2x2
x = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))(x)
# 随机丢弃四分之一的网络连接,防止过拟合
x = Dropout(0.25)(x)
# 第三个卷积层,64个卷积核,大小3x3,卷积模式SAME,激活函数prelu
x = Conv2D(filters=64, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding="same", name="conv3")(x)
# 第四个卷积层,64个卷积核,大小3x3,卷积模式SAME,激活函数prelu
x = Conv2D(filters=64, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding="same", name="conv4")(x)
# 第二层池化层,池化核大小2x2
x = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))(x)
# 随机丢弃四分之一的网络连接,防止过拟合
x = Dropout(0.25)(x)
# 第五个卷积层,128个卷积核,大小3x3,卷积模式SAME,激活函数prelu
x = Conv2D(filters=128, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding="same", name="conv5")(x)
# 第六个卷积层,128个卷积核,大小3x3,卷积模式SAME,激活函数prelu
x = Conv2D(filters=128, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding="same", name="conv6")(x)
# 第三层池化层,池化核大小2x2
x = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))(x)
# 随机丢弃四分之一的网络连接,防止过拟合
x = Dropout(0.25)(x)
# 全连接层,展开操作
x = Flatten()(x)
# 添加隐藏层神经元的数量和激活函数
x = Dense(512, name="full1")(x)
x = PReLU()(x)
x = Dense(256, name="full2")(x)
x = PReLU()(x)
# 输出层
x = Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax', name="output")(x)
model = Model(inputs=input_layer, outputs=x)
return model
2.2 查看一下模型结构
Keras支持使用summary来查看模型结构
model = build_model()
model.summary()
3 训练模型
3.1 划分训练集和测试集
借助sklearn的train_test_split来将数据集划分成训练集和测试集,使用train_test_split的好处是它可以按每个label都均匀划分数据集
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_data = img_train / 255
Y_data = to_categorical(img_label)
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_data, Y_data, test_size=0.1)
print("x_train.shape = ", x_train.shape)
print("y_train.shape = ", y_train.shape)
print("x_test.shape = ", x_test.shape)
print("y_test.shape = ", y_test.shape)
3.2 数据增强
数据增强的作用通常是为了扩充训练数据量提高模型的泛化能力,同时通过增加了噪声数据提升模型的鲁棒性。
train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rotation_range=9,
zoom_range=0.25,
width_shift_range=0.25,
height_shift_range=0.25
)
train_datagen.fit(x_train)
3.3 ModelCheckpoint和ReduceLROnPlateau设置
ModelCheckpoint可以帮助我们保存在训练过程中模型在测试集上效果最好的模型
ReduceLROnPlateau可以根据模型训练情况自动降低学习率
learning_rate_reduction = ReduceLROnPlateau(monitor='val_accuracy', patience=5, verbose=1, factor=0.5, min_lr=0.00001)
checkpoint = ModelCheckpoint("bestmodel.model", monitor='val_accuracy', verbose=1, save_best_only=True)
3.4 optimizer设置
sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, momentum=0.0, decay=0.0, nesterov=False)
3.5 编译模型
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer=sgd, metrics=['accuracy'])
3.6 训练模型
epochs = 120
batch_size = 128
history = model.fit_generator(
train_datagen.flow(x_train, y_train, batch_size=batch_size),
steps_per_epoch=x_train.shape[0] // batch_size,
epochs=epochs,
validation_data=(x_test, y_test),
callbacks=[checkpoint, learning_rate_reduction])
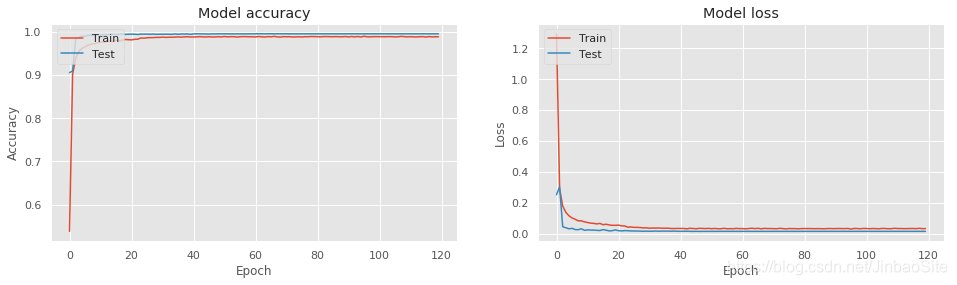
3.7 训练结果
绘制loss曲线和accuracy曲线
plt.style.use("ggplot")
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 4))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(history.history['accuracy'])
plt.plot(history.history['val_accuracy'])
plt.title('Model accuracy')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.legend(['Train', 'Test'], loc='upper left')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(history.history['loss'])
plt.plot(history.history['val_loss'])
plt.title('Model loss')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.legend(['Train', 'Test'], loc='upper left')
plt.show()
4 测试集图片
4.1 预测测试集
results=model.predict(img_test/255.0)
results=np.argmax(results, axis=1)
4.2 查看测试结果
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
show_img = 0
for idx in range(img_test.shape[0]):
plt.subplot(5, 5, show_img + 1)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.grid(False)
plt.imshow(img_test[idx].reshape(28, 28), cmap=plt.cm.binary)
plt.title("predict: %d" % results[idx])
show_img += 1
if show_img % 25 == 0:
break

5 提交结果
sub=pd.DataFrame()
sub['id']=list(test_data.values[0:,0])
sub['label']=results
sub.to_csv("submission.csv", index=False)
最后结果在0.98920,排名在106/1202
完整代码地址: Kannada-MNIST 如果你觉得我写的可以为你带来帮助,请给我一个Star